Modeler#
The AEDT 3D and 2D Modelers use object-oriented programming to create and manage objects. You can use getters and setters to create an object and change its properties.
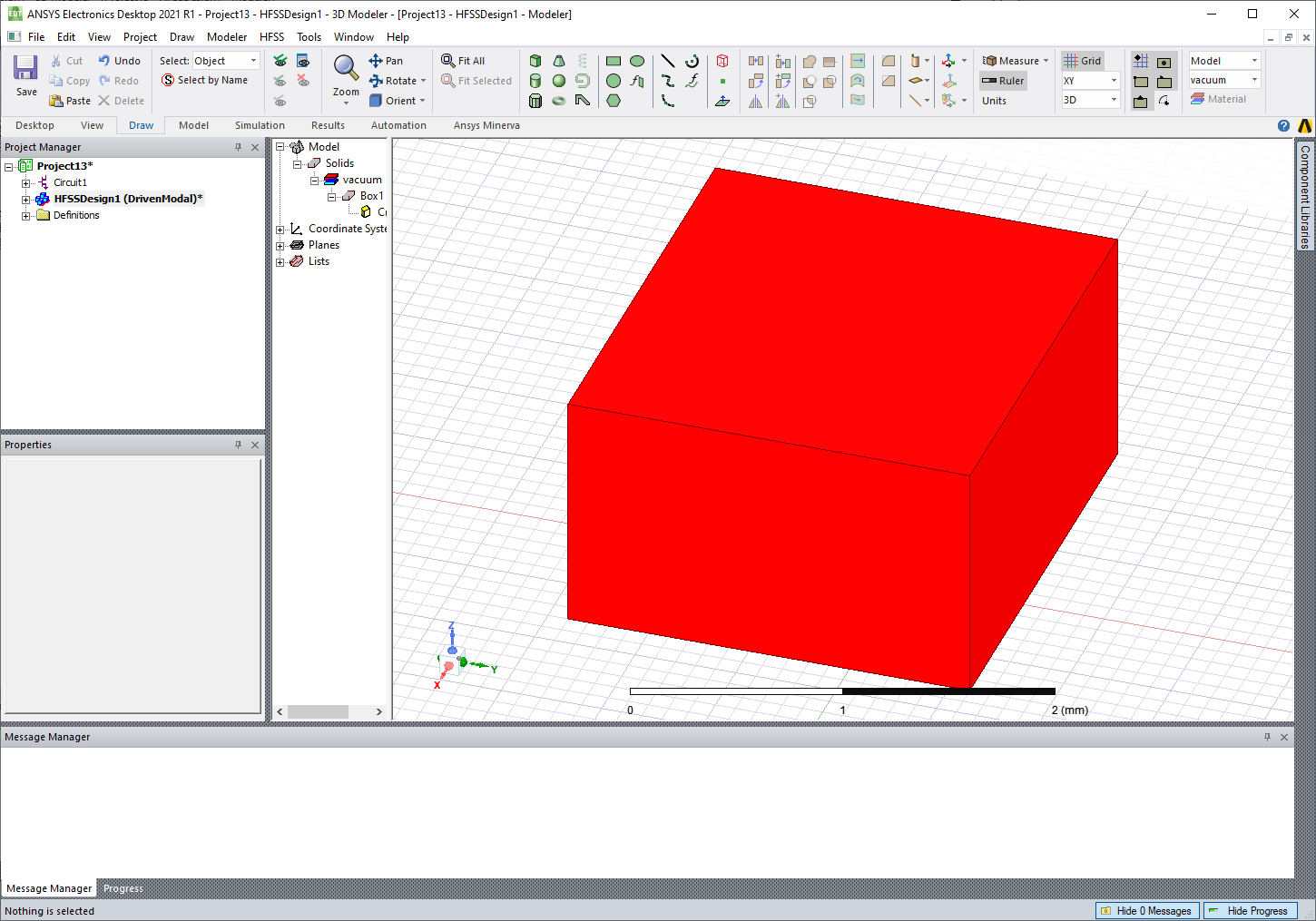
The following code creates a box and changes the color to red:
from ansys.aedt.core.hfss import Hfss
hfss = Hfss()
box = hfss.modeler.create_box(
origin=[0, 0, 0], sizes=[10, 10, 10], name="mybox", material="aluminum"
)
print(box.faces)
box.color = "Red"
Similarly, you can change other properties, such as the material and transparency.
box.material_name = "copper"
box.transparency = 0.4
print(box.material_name)
Once an object is created or is present in the design (from a loaded project), you can use a getter to get the related object. A getter works either with an object ID or object name. The object returned has all features, even if it has not been created in PyAEDT.
This example shows how easily you can go deeper into edges and vertices of faces or 3D objects:
box = hfss.modeler["mybox"]
for face in box.faces:
print(face.center)
for edge in face.edges:
print(edge.midpoint)
for vertice in edge.vertices:
print(vertice.position)
for vertice in box.vertices:
print(vertice.position)
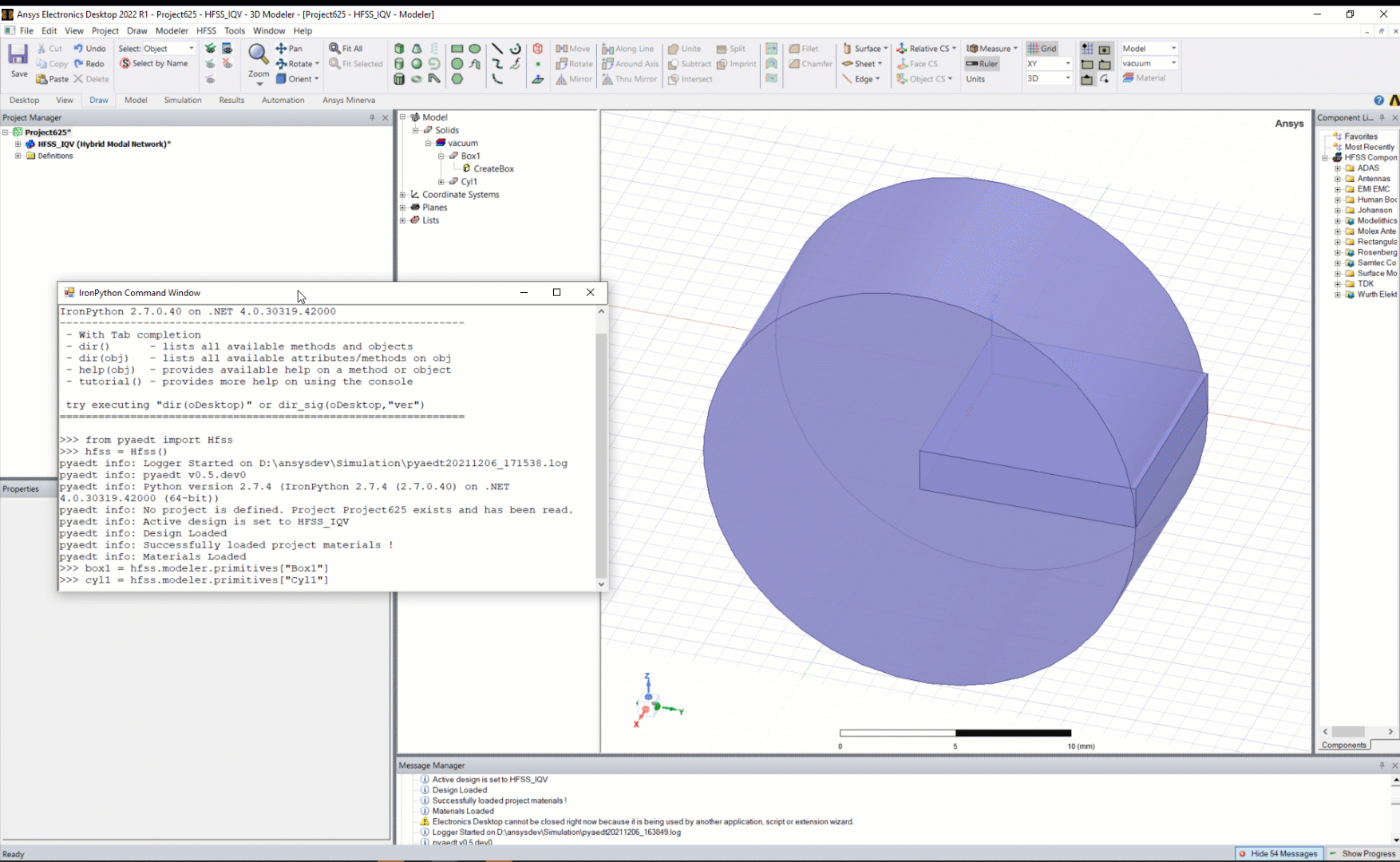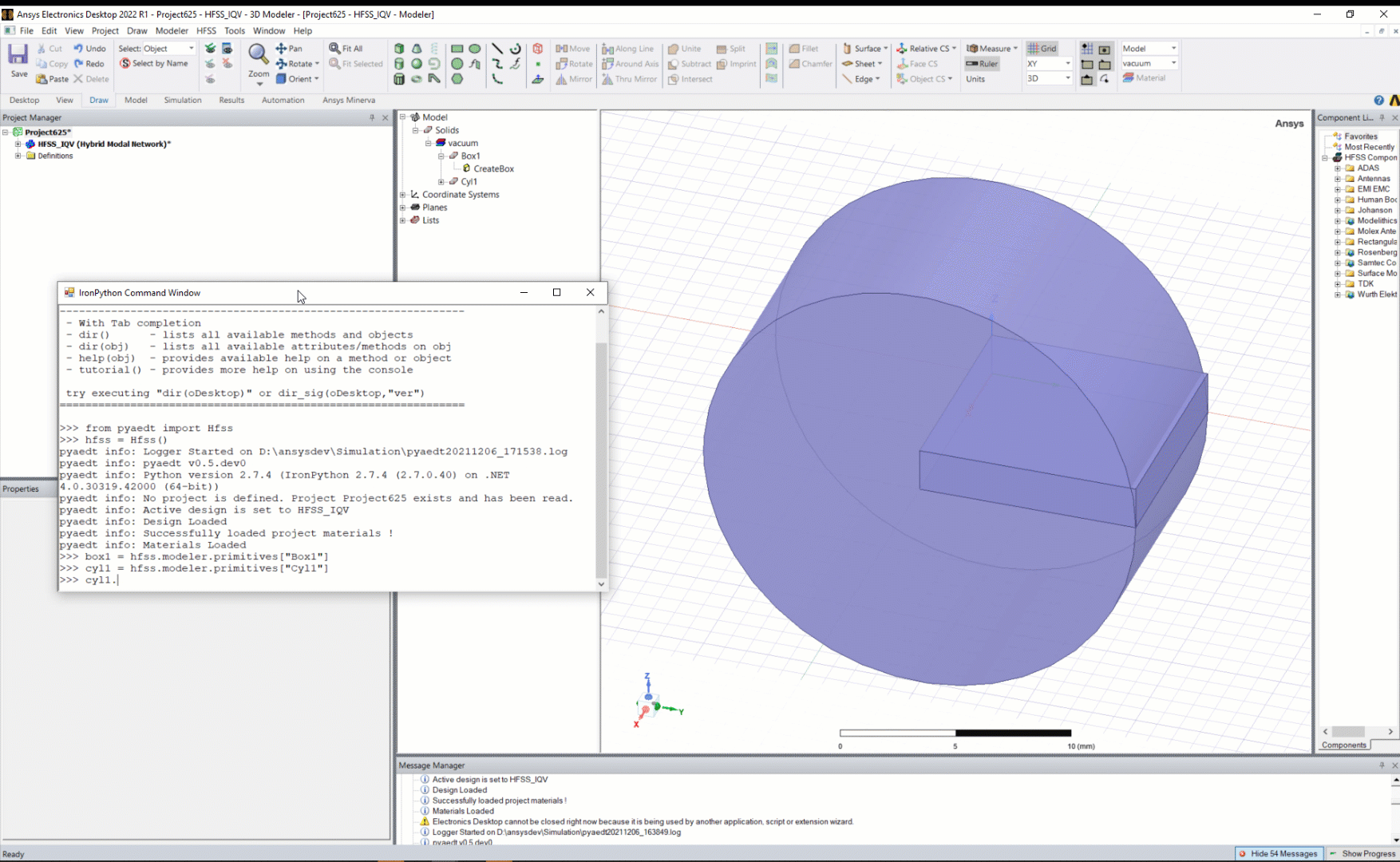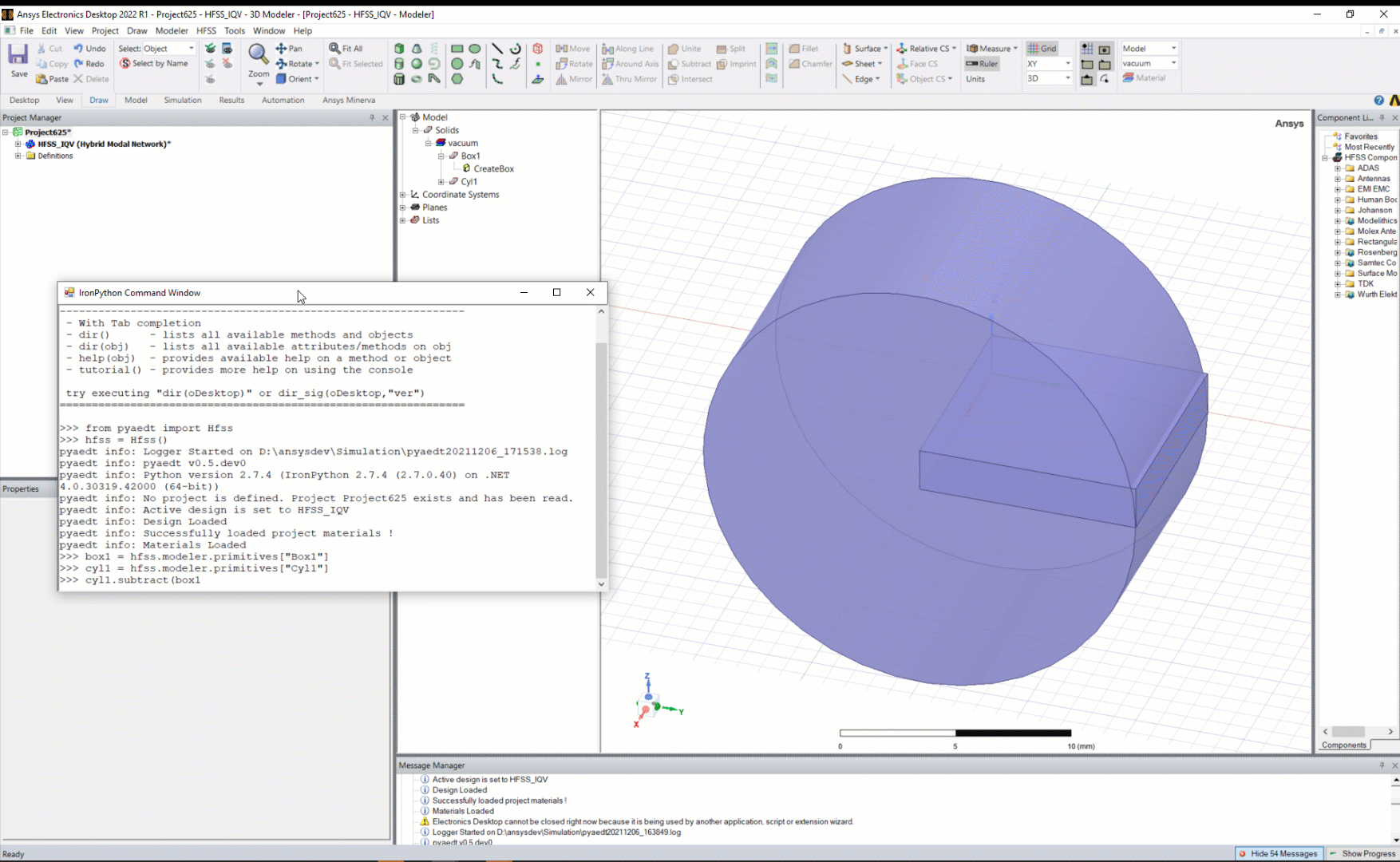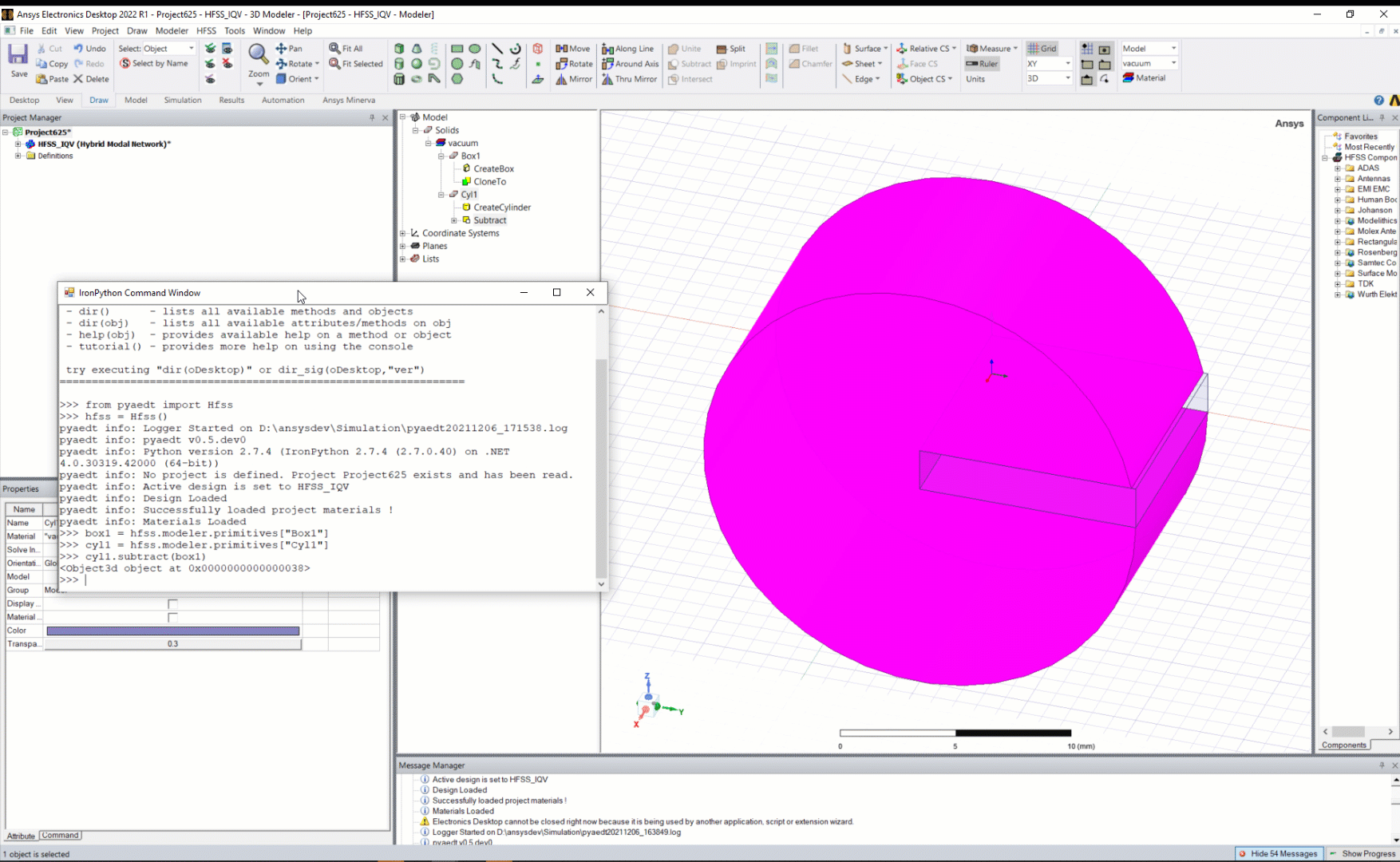
All objects support executing any modeler operation, such as union or subtraction:
box = hfss.modeler["mybox2"]
cyl = hfss.modeler["mycyl"]
box.unite(cyl)
box.subtract(cyl)