Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Create a 3D Component and reuse it#
Summary of the workflow 1. Create an antenna using PyAEDT and HFSS 3D Modeler (same can be done with EDB and HFSS 3D Layout) 2. Store the object as a 3D Component on the disk 3. Reuse the 3D component in another project 4. Parametrize and optimize target design
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports.
import os
import tempfile
from pyaedt import Hfss
from pyaedt.generic.general_methods import generate_unique_name
Set AEDT version#
Set AEDT version.
aedt_version = "2024.1"
Launch HFSS#
PyAEDT can initialize a new session of Electronics Desktop or connect to an existing one. Once Desktop is connected, a new HFSS session is started and a design is created.
hfss = Hfss(version=aedt_version, new_desktop=True, close_on_exit=True)
Variables#
PyAEDT can create and store all variables available in AEDT (Design, Project, Post Processing)
hfss["thick"] = "0.1mm"
hfss["width"] = "1mm"
Modeler#
PyAEDT supports all modeler functionalities available in the Desktop. Objects can be created, deleted and modified using all available boolean operations. History is also fully accessible to PyAEDT.
substrate = hfss.modeler.create_box(["-width", "-width", "-thick"], ["2*width", "2*width", "thick"], name="sub",
material="FR4_epoxy")
patch = hfss.modeler.create_rectangle("XY",["-width/2","-width/2","0mm"],["width","width"], name="patch1")
via1 = hfss.modeler.create_cylinder(2, ["-width/8", "-width/4", "-thick"], "0.01mm", "thick", name="via_inner",
material="copper")
via_outer = hfss.modeler.create_cylinder(2, ["-width/8", "-width/4", "-thick"], "0.025mm", "thick", name="via_teflon",
material="Teflon_based")
Boundaries#
Most of HFSS boundaries and excitations are already available in PyAEDT. User can assign easily a boundary to a face or to an object by taking benefits of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) available in PyAEDT.
hfss.assign_perfecte_to_sheets(patch)
<pyaedt.modules.Boundary.BoundaryObject object at 0x00000187B5C46920>
Advanced Modeler functions#
Thanks to Python capabilities a lot of additional functionalities have been added to the Modeler of PyAEDT. in this example there is a property to retrieve automatically top and bottom faces of an objects.
<pyaedt.modules.Boundary.BoundaryObject object at 0x00000187B5C468C0>
Create Wave Port#
Wave port can be assigned to a sheet or to a face of an object.
hfss.wave_port(via_outer.bottom_face_z, name="P1")
False
Create 3D Component#
Once the model is ready a 3D Component can be created. Multiple options are available to partially select objects, cs, boundaries and mesh operations. Furthermore, encrypted 3d comp can be created too.
component_path = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), generate_unique_name("component_test") + ".aedbcomp")
hfss.modeler.create_3dcomponent(component_path, "patch_antenna")
True
Multiple project management#
PyAEDT allows to control multiple projects, design and solution type at the same time.
hfss2 = Hfss(project="new_project", design="new_design")
Insert of 3d component#
The 3d component can be inserted without any additional info. All needed info will be read from the file itself.
hfss2.modeler.insert_3d_component(component_path)
<pyaedt.modeler.cad.components_3d.UserDefinedComponent object at 0x00000187CD49E8F0>
3D Component Parameters#
All 3d Component parameters are available and can be parametrized.
hfss2.modeler.user_defined_components["patch_antenna1"].parameters
hfss2["p_thick"] = "1mm"
hfss2.modeler.user_defined_components["patch_antenna1"].parameters["thick"]="p_thick"
Multiple 3d Components#
There is no limit to the number of 3D components that can be added on the same design. They can be the same or linked to different files.
hfss2.modeler.create_coordinate_system(origin=[20, 20, 10], name="Second_antenna")
ant2 = hfss2.modeler.insert_3d_component(component_path, coordinate_system="Second_antenna")
Move components#
The component can be moved by changing is position or moving the relative coordinate system.
hfss2.modeler.coordinate_systems[0].origin = [10, 10, 3]
Boundaries#
Most of HFSS boundaries and excitations are already available in PyAEDT. User can assign easily a boundary to a face or to an object by taking benefits of
hfss2.modeler.create_air_region(30, 30, 30, 30, 30, 30)
hfss2.assign_radiation_boundary_to_faces(hfss2.modeler["Region"].faces)
# Create Setup and Optimetrics
# Once project is ready to be solved, a setup and parametrics analysis can be created with PyAEDT.
# All setup parameters can be edited.
setup1 = hfss2.create_setup()
optim = hfss2.parametrics.add("p_thick", "0.2mm", "1.5mm", step=14)
Save project#
Save the project.
hfss2.modeler.fit_all()
hfss2.plot(show=False, output_file=os.path.join(hfss.working_directory, "Image.jpg"), plot_air_objects=True)
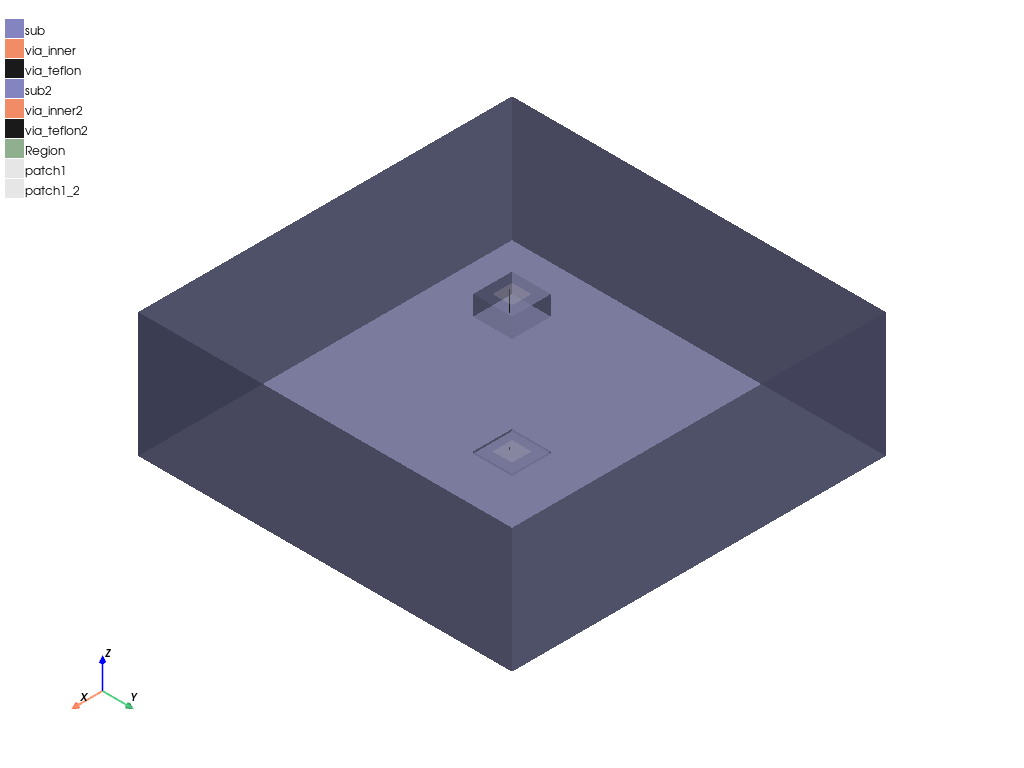
<pyaedt.generic.plot.ModelPlotter object at 0x00000187CD49CD60>
Close AEDT#
After the simulation completes, you can close AEDT or release it using the
pyaedt.Desktop.release_desktop() method.
All methods provide for saving the project before closing AEDT.
hfss2.save_project(os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), generate_unique_name("parametrized") + ".aedt"))
hfss2.release_desktop()
True
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 39.930 seconds)