Advanced#
You can use PyAEDT for postprocessing of AEDT results to display graphics object and plot data.
Touchstone#
TouchstoneData class is based on scikit-rf package and allows advanced touchstone post-processing. The following methods allows to read and check touchstone files.
Get all insertion losses. |
|
Plot all insertion losses. |
|
Plot a list of curves. |
|
Plot all return losses. |
|
Transform network from single ended parameters to generalized mixed mode parameters. |
|
Get the list of all the return loss from a list of excitations. |
|
Get the list of all the insertion losses from prefix. |
|
Get the list of all the Near End XTalk a list of excitation. |
|
Get the list of all the Far End XTalk from a list of excitations and a prefix that will be used to retrieve driver and receivers names. |
|
Plot all next crosstalk curves. |
|
Plot all fext crosstalk curves. |
|
Analyze a solution data object with multiple curves and find the worst curve. |
|
Load the contents of a Touchstone file into an NPort. |
|
Check passivity and causality for all Touchstone files included in the folder. |
|
Get all Touchstone files in a directory. |
Here an example on how to use TouchstoneData class.
from ansys.aedt.core.visualization.advanced.touchstone_parser import TouchstoneData
ts1 = TouchstoneData(touchstone_file=os.path.join(test_T44_dir, "port_order_1234.s8p"))
assert ts1.get_mixed_mode_touchstone_data()
ts2 = TouchstoneData(touchstone_file=os.path.join(test_T44_dir, "port_order_1324.s8p"))
assert ts2.get_mixed_mode_touchstone_data(port_ordering="1324")
assert ts1.plot_insertion_losses(plot=False)
assert ts1.get_worst_curve(curve_list=ts1.get_return_loss_index(), plot=False)
Farfield#
PyAEDT offers sophisticated tools for advanced farfield post-processing.
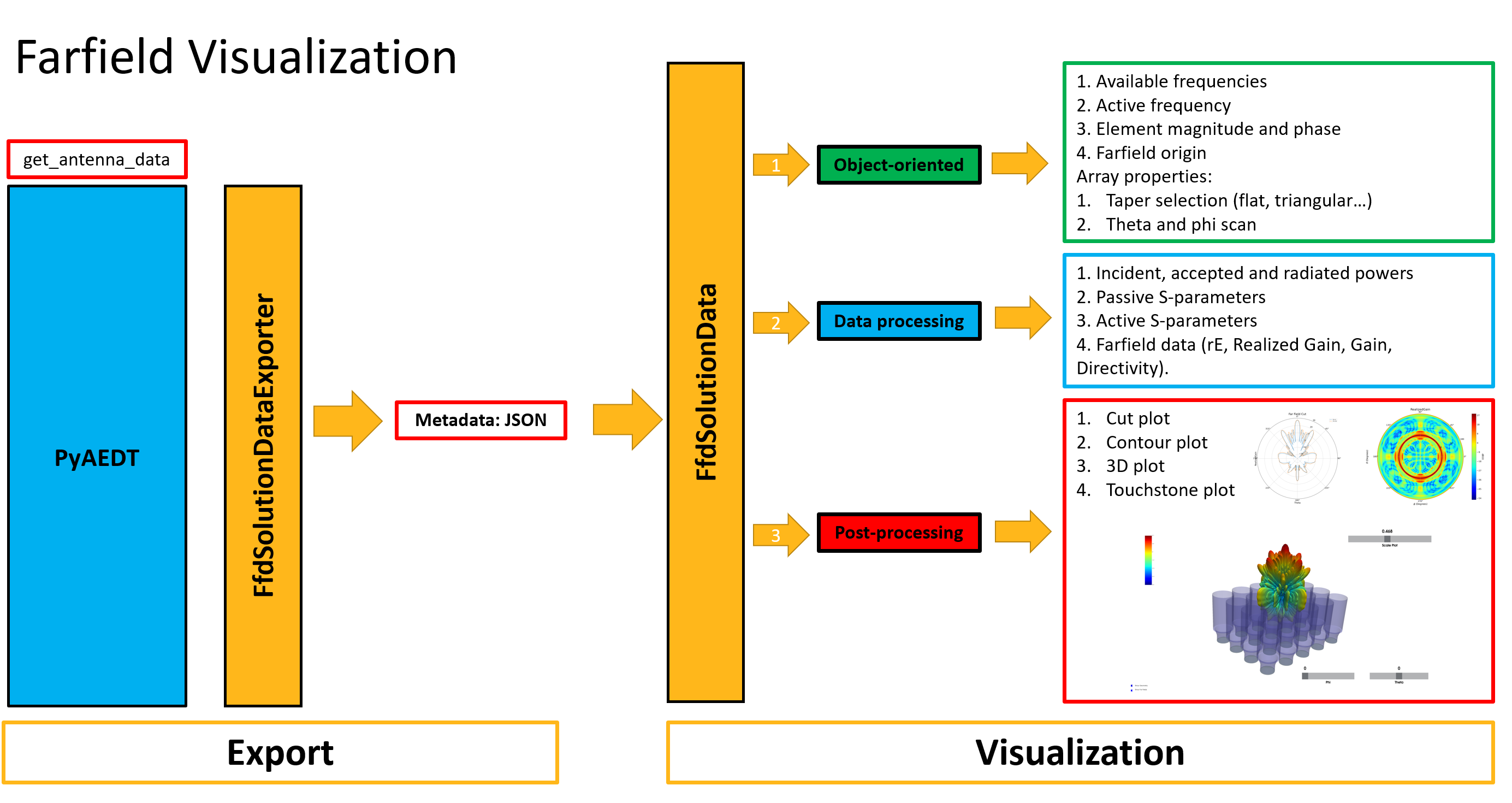
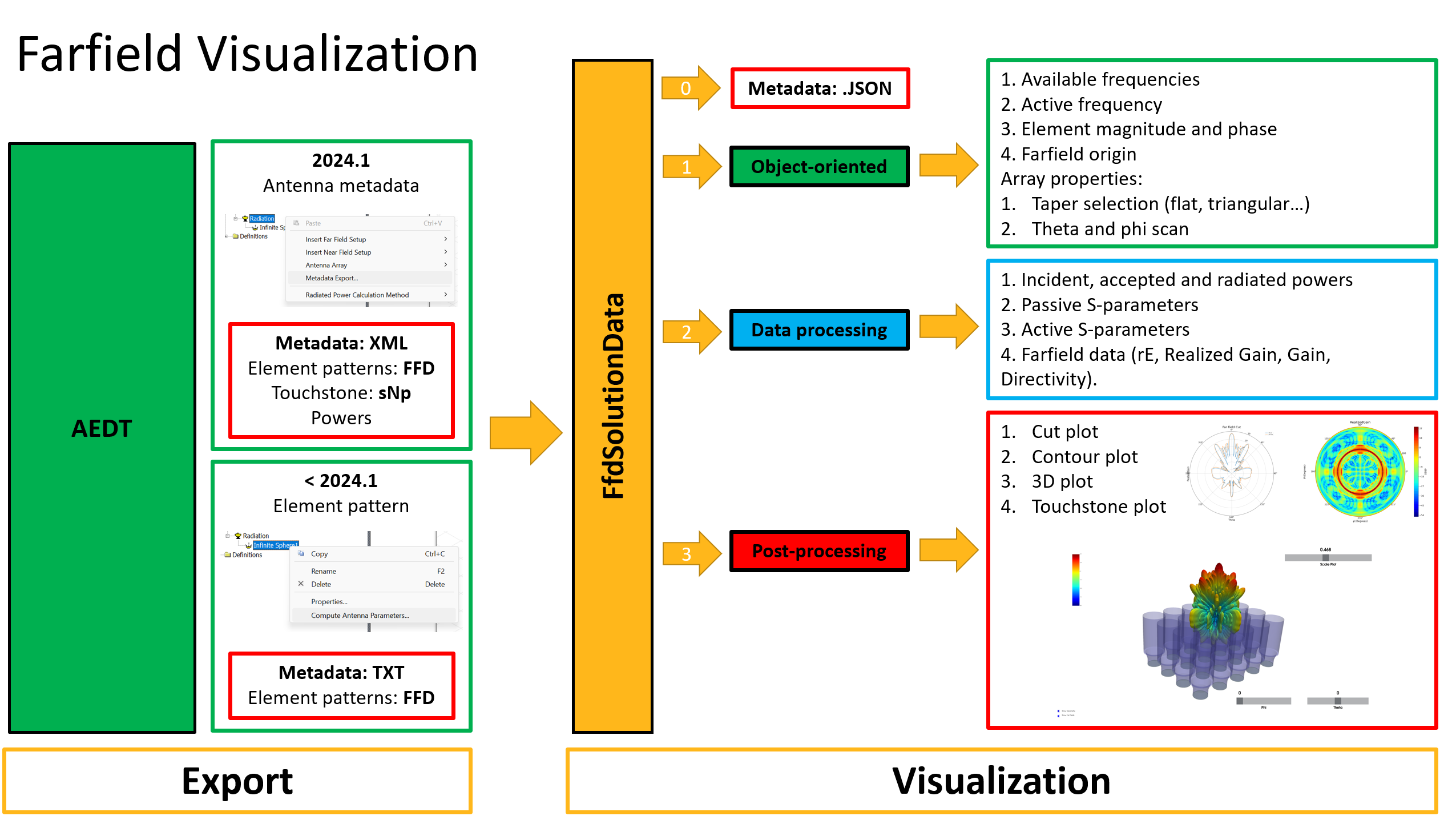
There are two complementary classes: FfdSolutionDataExporter and FfdSolutionData.
FfdSolutionDataExporter: Enables efficient export and manipulation of farfield data. It allows users to convert simulation results into a standard metadata format for further analysis, or reporting.
FfdSolutionData: Focuses on the direct access and processing of farfield solution data. It supports a comprehensive set of postprocessing operations, from visualizing radiation patterns to computing key performance metrics.
Provides antenna far-field data. |
This code shows how you can get the farfield data and perform some post-processing:
import ansys.aedt.core
from ansys.aedt.core.generic.farfield_visualization import FfdSolutionDataExporter
app = ansys.aedt.core.Hfss()
ffdata = app.get_antenna_data(
frequencies=None,
setup="Setup1 : Sweep",
sphere="3D",
variations=None,
overwrite=False,
link_to_hfss=True,
export_touchstone=True,
)
incident_power = ffdata.incident_power
ffdata.plot_cut(primary_sweep="Theta", theta=0)
ffdata.plot_contour(polar=True)
ffdata.plot_3d(show_geometry=False)
app.release_desktop(False, False)
If you exported the farfield data previously, you can directly get the farfield data:
from ansys.aedt.core.generic.farfield_visualization import FfdSolutionData
input_file = r"path_to_ffd\pyaedt_antenna_metadata.json"
ffdata = FfdSolutionData(input_file)
incident_power = ffdata.incident_power
ffdata.plot_cut(primary_sweep="Theta", theta=0)
ffdata.plot_contour(polar=True)
ffdata.plot_3d(show_geometry=False)
app.release_desktop(False, False)
The following diagram shows both classes work. You can use them independently or from the get_antenna_data method.
If you have existing farfield data, or you want to export it manually, you can still use FfdSolutionData class.
Monostatic RCS#
PyAEDT provides tools for exporting monostatic radar cross section (RCS) data through the MonostaticRCSExporter class.
For advanced RCS post-processing, analysis, and visualization, use the Radar Explorer Toolkit.
Note
Advanced RCS features (MonostaticRCSData and MonostaticRCSPlotter) have been moved to the
Radar Explorer Toolkit.
Install the toolkit with:
pip install ansys-aedt-toolkits-radar-explorer
PyAEDT RCS exporter#
The MonostaticRCSExporter class enables efficient export of RCS simulation data into a standardized
metadata format for further analysis with the Radar Explorer Toolkit.
Class to enable export of radar cross-section (RCS) data from HFSS. |
Export RCS data from HFSS:
from ansys.aedt.core import Hfss
app = Hfss()
setup_name = "Setup1 : LastAdaptive"
frequencies = [77e9]
# Export RCS data
rcs_exporter = app.get_rcs_data(
frequencies=frequencies, setup=setup_name, variation_name="rcs_solution"
)
# Metadata file is created for use with Radar Explorer Toolkit
metadata_file = rcs_exporter.metadata_file
Radar explorer toolkit#
For comprehensive RCS analysis and visualization, use the radar explorer toolkit:
MonostaticRCSData: Advanced processing of RCS solution data with support for range profiles, waterfall plots, and ISAR imaging.
MonostaticRCSPlotter: Interactive 3D visualization and post-processing of RCS data.
Example using the radar explorer toolkit:
# Install first: pip install ansys-aedt-toolkits-radar-explorer
from ansys.aedt.toolkits.radar_explorer.rcs_visualization import MonostaticRCSData
from ansys.aedt.toolkits.radar_explorer.rcs_visualization import MonostaticRCSPlotter
# Load RCS data exported from PyAEDT
input_file = r"path_to_data\pyaedt_rcs_metadata.json"
rcs_data = MonostaticRCSData(input_file)
# Create plotter for visualization
rcs_plotter = MonostaticRCSPlotter(rcs_data)
# Generate various plots
rcs_plotter.plot_rcs(primary_sweep="IWavePhi")
rcs_plotter.plot_3d()
rcs_plotter.add_range_profile()
rcs_plotter.plot_scene()
For complete documentation and API reference, see:
FRTM processing#
PyAEDT offers sophisticated tools for FRTM post-processing.
There are two complementary classes: FRTMData, and FRTMPlotter.
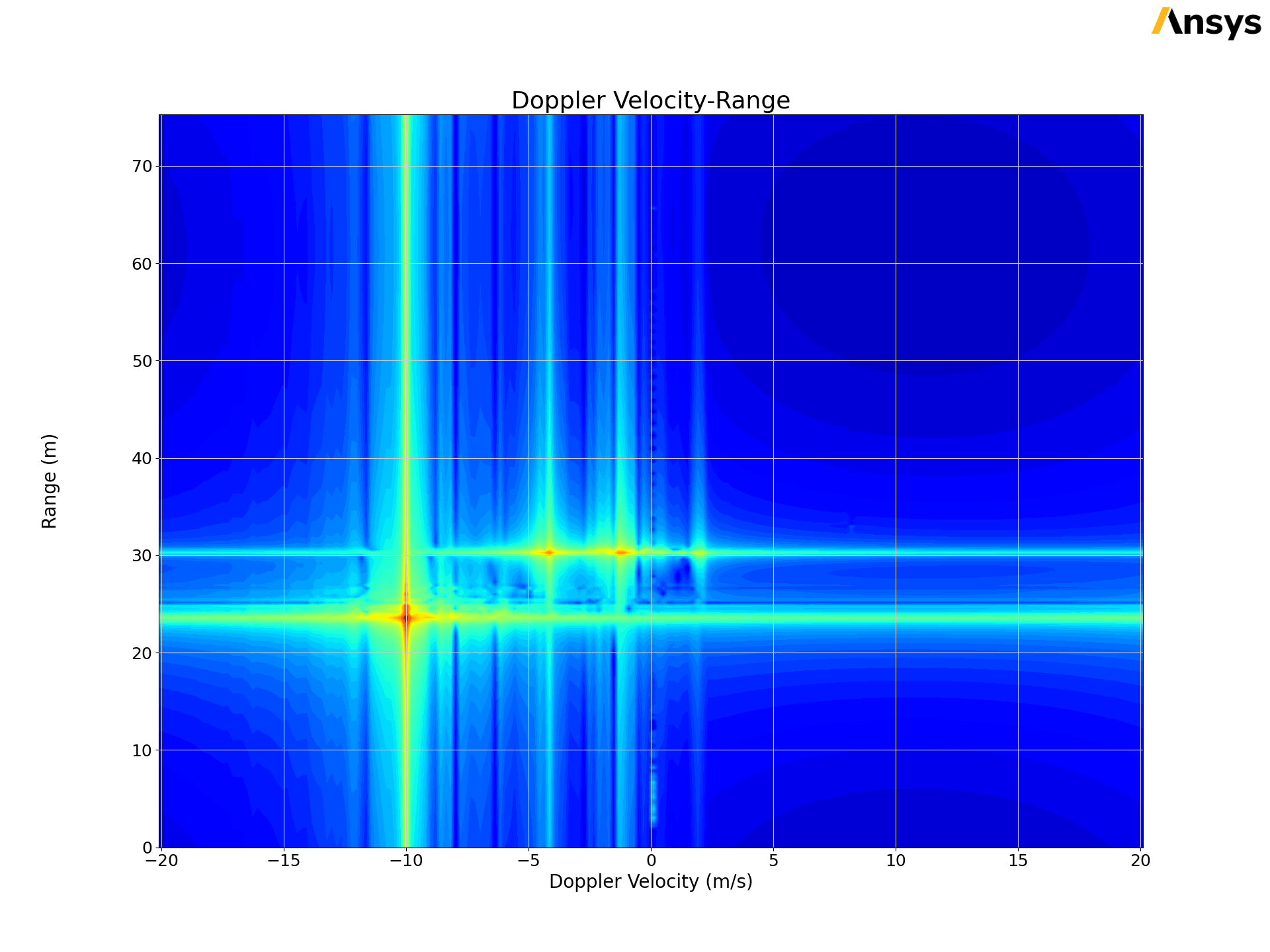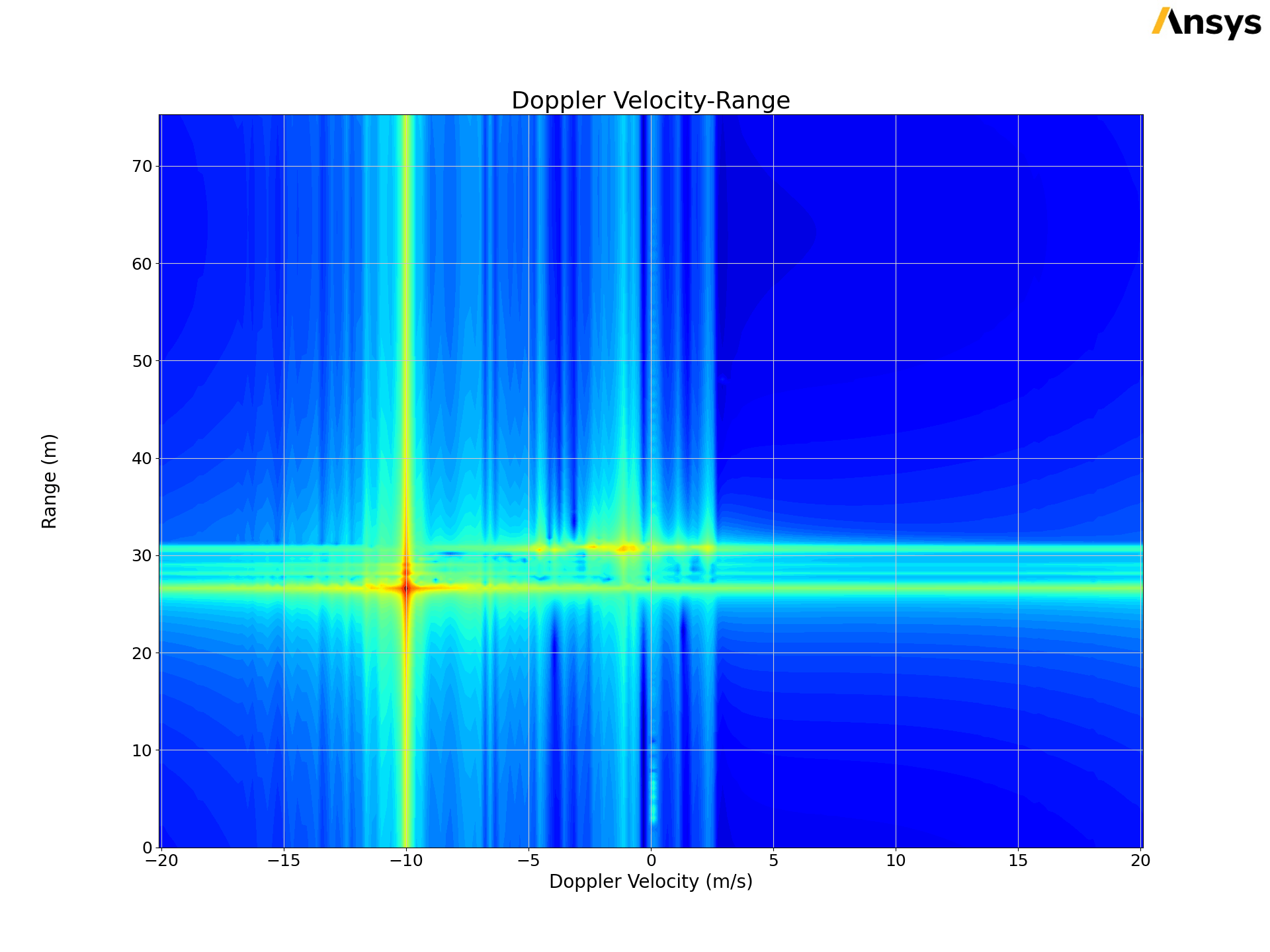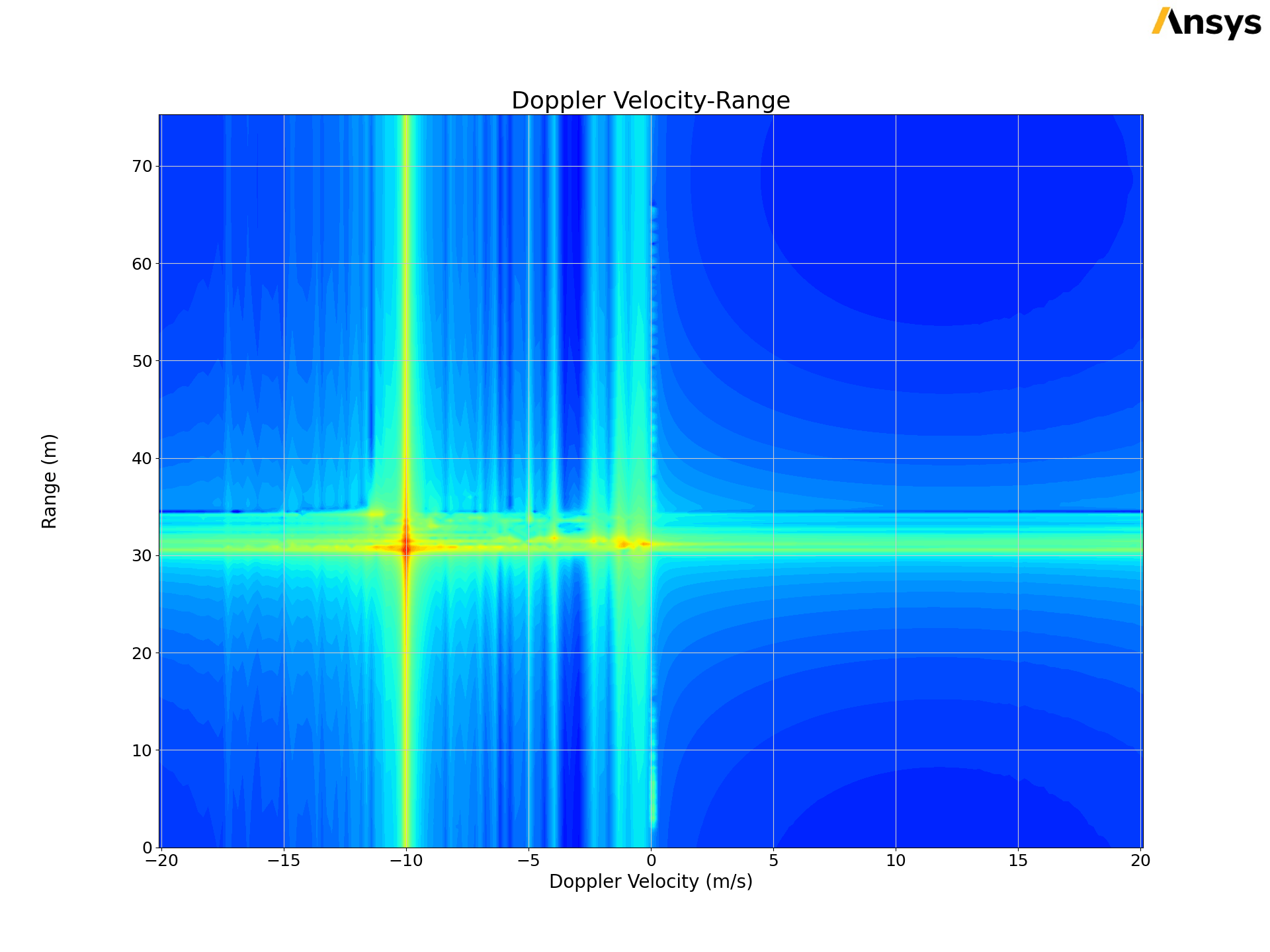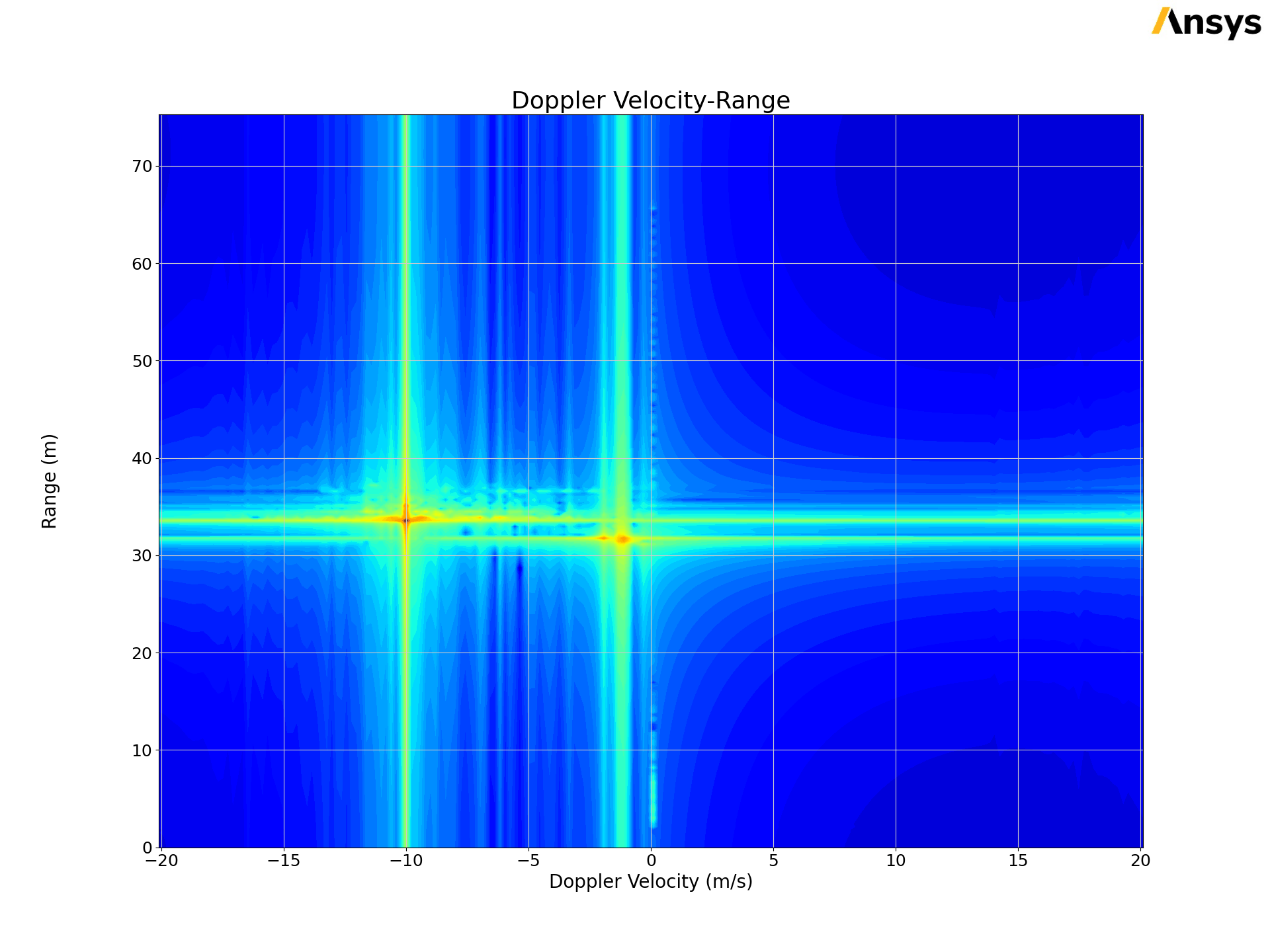
FRTMData: Focuses on the direct access and processing of FRTM solution data. It supports a comprehensive set of postprocessing operations, like range profile and range doppler processing.
FRTMPlotter: Focuses on the post-processing of FRTM solution data.
Provides FRTM data. |
|
Provides range doppler data. |
This code shows how you can get the FRTM data:
from ansys.aedt.core.visualization.advanced.frtm_visualization import FRTMPlotter
from ansys.aedt.core.visualization.advanced.frtm_visualization import FRTMData
input_dir = r"path_to_data"
doppler_data_frames = {}
frames_dict = get_results_files(input_dir)
for frame, data_frame in frames_dict.items():
doppler_data = FRTMData(data_frame)
doppler_data_frames[frame] = doppler_data
frtm_plotter = FRTMPlotter(doppler_data_frames)
frtm_plotter.plot_range_doppler()
The following picture shows the output of the previous code.
Heterogeneous data message#
Heterogeneous data message (HDM) is the file exported from SBR+ solver containing rays information. The following methods allows to read and plot rays information.
Manages Hdm data to be plotted with |
|
Parser class that loads an HDM-format export file from HFSS SBR+, interprets its header and its binary content. |
Open street map#
PyAEDT provides comprehensive tools for importing and processing OpenStreetMap (OSM) data to create realistic 3D environments for electromagnetic simulations. The OSM module enables automatic generation of buildings, roads, and terrain meshes suitable for large-scale RF propagation and antenna placement studies.
The module consists of three main preparation classes:
BuildingsPrep: Generates 3D building models from OSM building footprints with estimated heights
RoadPrep: Creates road network geometries with proper elevation mapping
TerrainPrep: Generates terrain meshes with elevation data
Contains all basic functions needed to generate buildings stl files. |
|
Contains all basic functions needed to generate road stl files. |
|
Contains all basic functions needed for creating a terrain stl mesh. |
|
Convert latitude and longitude to UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) coordinates. |
|
Convert UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) coordinates to latitude and longitude. |
Use the high-level import_from_openstreet_map method to import complete OSM scenes:
from ansys.aedt.core import Hfss
app = Hfss()
# Define location (latitude, longitude)
center = [40.7128, -74.0060] # New York City
# Import OSM data with buildings, roads, and terrain
scene = app.modeler.import_from_openstreet_map(
latitude_longitude=center,
terrain_radius=500,
include_osm_buildings=True,
including_osm_roads=True,
import_in_aedt=True,
)
For advanced control, use the preparation classes directly:
from ansys.aedt.core.modeler.advanced_cad.osm import (
BuildingsPrep,
RoadPrep,
TerrainPrep,
)
# Define location
center = [40.7128, -74.0060] # New York City
output_path = "./osm_output"
# Generate terrain
terrain_prep = TerrainPrep(cad_path=output_path)
terrain_data = terrain_prep.get_terrain(center, max_radius=500, grid_size=30)
# Generate buildings aligned to terrain
building_prep = BuildingsPrep(cad_path=output_path)
building_data = building_prep.generate_buildings(
center, terrain_data["mesh"], max_radius=400
)
# Generate roads aligned to terrain
road_prep = RoadPrep(cad_path=output_path)
road_data = road_prep.create_roads(
center, terrain_data["mesh"], max_radius=500, road_width=8
)
The module automatically:
Downloads geographic data from OpenStreetMap
Converts coordinates from lat/lon to local UTM system
Generates 3D STL meshes for buildings, roads, and terrain
Aligns all geometries to terrain elevation
Exports files ready for AEDT import
Note
Building heights are estimated from OSM building:levels tags or height attributes.
Large radius values may result in significant download and processing times.
For complete documentation, see the example: City scenario with OpenStreetMap
Miscellaneous#
PyAEDT has additional advanced post-processing features:
Convert a near field data folder to hfss nfd file and link it to and file. |
|
Parse Ansys report '.rdat' file. |