Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
HFSS: spiral inductor#
This example shows how you can use PyAEDT to create a spiral inductor, solve it, and plot results.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports.
import os
import pyaedt
project_name = pyaedt.generate_unique_project_name(project_name="spiral")
Set AEDT version#
Set AEDT version.
aedt_version = "2024.1"
Set non-graphical mode#
Set non-graphical mode.
You can set non_graphical either to True or False.
non_graphical = False
Launch HFSS#
Launch HFSS 2023 R2 in non-graphical mode and change the units to microns.
hfss = pyaedt.Hfss(specified_version=aedt_version, non_graphical=non_graphical, designname="A1",
new_desktop_session=True)
hfss.solution_type = "Modal"
hfss.modeler.model_units = "um"
p = hfss.modeler
Define variables#
Define input variables. You can use the values that follow or edit them.
Standardize polyline#
Standardize the polyline using the create_line method to fix
the width, thickness, and material.
Create spiral inductor#
Create the spiral inductor. This spiral inductor is not parametric, but you could parametrize it later.
Center return path#
Center the return path.
<pyaedt.modeler.cad.object3d.Object3d object at 0x000002264CBD25C0>
Create port 1#
Create port 1.
p.create_rectangle(orientation=pyaedt.constants.PLANE.YZ,
origin=[abs(x1) + 5, y0 - width / 2, -gap - thickness / 2],
sizes=[width, "-Tsub+{}{}".format(gap, hfss.modeler.model_units)],
name="port1"
)
hfss.lumped_port(assignment="port1", integration_line=pyaedt.constants.AXIS.Z)
<pyaedt.modules.Boundary.BoundaryObject object at 0x000002264CBD0E50>
Create port 2#
Create port 2.
<pyaedt.modules.Boundary.BoundaryObject object at 0x000002264CBD2590>
Create silicon substrate and ground plane#
Create the silicon substrate and the ground plane.
<pyaedt.modeler.cad.object3d.Object3d object at 0x000002264CBD3AF0>
Assign airbox and radiation#
Assign the airbox and the radiation.
<pyaedt.modules.Boundary.BoundaryObject object at 0x000002264CBD1B10>
Assign material override#
Assign a material override so that the validation check does not fail.
hfss.change_material_override()
True
Plot model#
Plot the model.
hfss.plot(show=False, export_path=os.path.join(hfss.working_directory, "Image.jpg"), plot_air_objects=False)
<pyaedt.generic.plot.ModelPlotter object at 0x000002265046A350>
Create setup#
Create the setup and define a frequency sweep to solve the project.
setup1 = hfss.create_setup(name="setup1")
setup1.props["Frequency"] = "10GHz"
hfss.create_linear_count_sweep(setup="setup1", units="GHz", start_frequency=1e-3, stop_frequency=50,
num_of_freq_points=451, sweep_type="Interpolating")
hfss.save_project()
hfss.analyze()
True
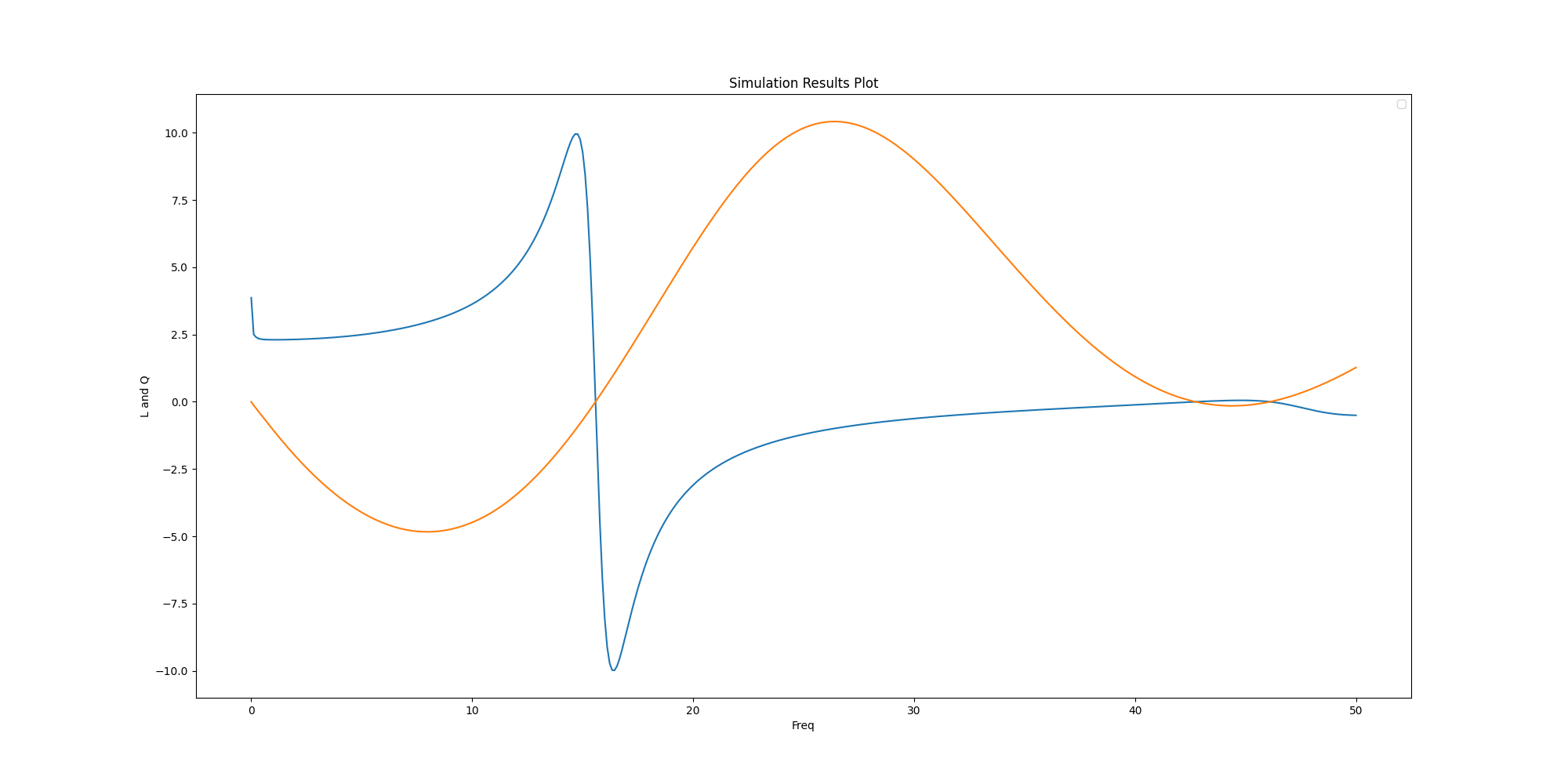
Get report data#
Get report data and use the following formulas to calculate the inductance and quality factor.
Create output variable#
Create output variable
hfss.create_output_variable("L", L_formula, solution="setup1 : LastAdaptive")
True
Plot calculated values in Matplotlib#
Plot the calculated values in Matplotlib.
No artists with labels found to put in legend. Note that artists whose label start with an underscore are ignored when legend() is called with no argument.
<Figure size 2000x1000 with 1 Axes>
Export results to csv file#
Export results to csv file
data.export_data_to_csv(os.path.join(hfss.toolkit_directory, "output.csv"))
True
Save project and close AEDT#
Save the project and close AEDT.
hfss.save_project(project_name)
hfss.release_desktop()
True
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 48.453 seconds)