Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Q3D Extractor: busbar analysis#
This example shows how you can use PyAEDT to create a busbar design in Q3D Extractor and run a simulation.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports.
import os
import pyaedt
Set non-graphical mode#
Set non-graphical mode.
You can set non_graphical either to True or False.
non_graphical = False
Set debugger mode#
PyAEDT allows to enable a debug logger which logs all methods called and argument passed. This example shows how to enable it.
pyaedt.settings.enable_debug_logger = True
pyaedt.settings.enable_debug_methods_argument_logger = True
pyaedt.settings.enable_debug_internal_methods_logger = False
Launch AEDT and Q3D Extractor#
Launch AEDT 2023 R2 in graphical mode and launch Q3D Extractor. This example uses SI units.
q = pyaedt.Q3d(projectname=pyaedt.generate_unique_project_name(),
specified_version="2023.2",
non_graphical=non_graphical,
new_desktop_session=True)
Initializing new desktop!
Create primitives#
Create polylines for three busbars and a box for the substrate.
b1 = q.modeler.create_polyline(
[[0, 0, 0], [-100, 0, 0]],
name="Bar1",
matname="copper",
xsection_type="Rectangle",
xsection_width="5mm",
xsection_height="1mm",
)
q.modeler["Bar1"].color = (255, 0, 0)
q.modeler.create_polyline(
[[0, -15, 0], [-150, -15, 0]],
name="Bar2",
matname="aluminum",
xsection_type="Rectangle",
xsection_width="5mm",
xsection_height="1mm",
)
q.modeler["Bar2"].color = (0, 255, 0)
q.modeler.create_polyline(
[[0, -30, 0], [-175, -30, 0], [-175, -10, 0]],
name="Bar3",
matname="copper",
xsection_type="Rectangle",
xsection_width="5mm",
xsection_height="1mm",
)
q.modeler["Bar3"].color = (0, 0, 255)
q.modeler.create_box([50, 30, -0.5], [-250, -100, -3], name="substrate", matname="FR4_epoxy")
q.modeler["substrate"].color = (128, 128, 128)
q.modeler["substrate"].transparency = 0.8
q.plot(show=False, export_path=os.path.join(q.working_directory, "Q3D.jpg"), plot_air_objects=False)
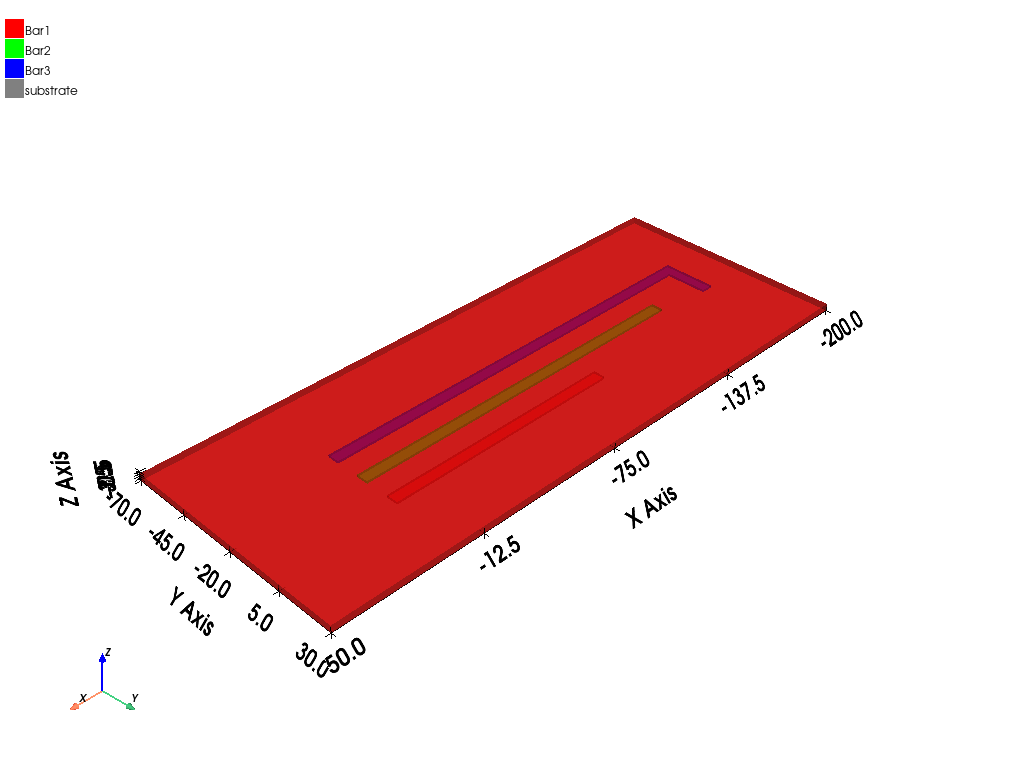
<pyaedt.generic.plot.ModelPlotter object at 0x000001D9A4263CD0>
Set up boundaries#
Identify nets and assign sources and sinks to all nets. There is a source and sink for each busbar.
q.auto_identify_nets()
q.source("Bar1", axisdir=q.AxisDir.XPos, name="Source1")
q.sink("Bar1", axisdir=q.AxisDir.XNeg, name="Sink1")
q.source("Bar2", axisdir=q.AxisDir.XPos, name="Source2")
q.sink("Bar2", axisdir=q.AxisDir.XNeg, name="Sink2")
q.source("Bar3", axisdir=q.AxisDir.XPos, name="Source3")
bar3_sink = q.sink("Bar3", axisdir=q.AxisDir.YPos)
bar3_sink.name = "Sink3"
Print information#
Use the different methods available to print net and terminal information.
print(q.nets)
print(q.net_sinks("Bar1"))
print(q.net_sinks("Bar2"))
print(q.net_sinks("Bar3"))
print(q.net_sources("Bar1"))
print(q.net_sources("Bar2"))
print(q.net_sources("Bar3"))
['Bar1', 'Bar2', 'Bar3']
['Sink1']
['Sink2']
['Sink3']
['Source1']
['Source2']
['Source3']
Create setup#
Create a setup for Q3D Extractor and add a sweep that defines the adaptive frequency value.
setup1 = q.create_setup(props={"AdaptiveFreq": "100MHz"})
sw1 = setup1.add_sweep()
sw1.props["RangeStart"] = "1MHz"
sw1.props["RangeEnd"] = "100MHz"
sw1.props["RangeStep"] = "5MHz"
sw1.update()
True
Get curves to plot#
Get the curves to plot. The following code simplifies the way to get curves.
data_plot_self = q.matrices[0].get_sources_for_plot(get_self_terms=True, get_mutual_terms=False)
data_plot_mutual = q.get_traces_for_plot(get_self_terms=False, get_mutual_terms=True, category="C")
data_plot_self
data_plot_mutual
['C(Bar1,Bar2)', 'C(Bar1,Bar3)', 'C(Bar2,Bar1)', 'C(Bar2,Bar3)', 'C(Bar3,Bar1)', 'C(Bar3,Bar2)']
Create rectangular plot#
Create a rectangular plot and a data table.
q.post.create_report(expressions=data_plot_self)
q.post.create_report(expressions=data_plot_mutual, context="Original", plot_type="Data Table")
<pyaedt.modules.report_templates.Standard object at 0x000001D9A42610F0>
Solve setup#
Solve the setup.
q.analyze()
q.save_project()
True
Get report data#
Get the report data into a data structure that allows you to manipulate it.
a = q.post.get_solution_data(expressions=data_plot_self, context="Original")
a.intrinsics["Freq"]
a.data_magnitude()
a.plot()
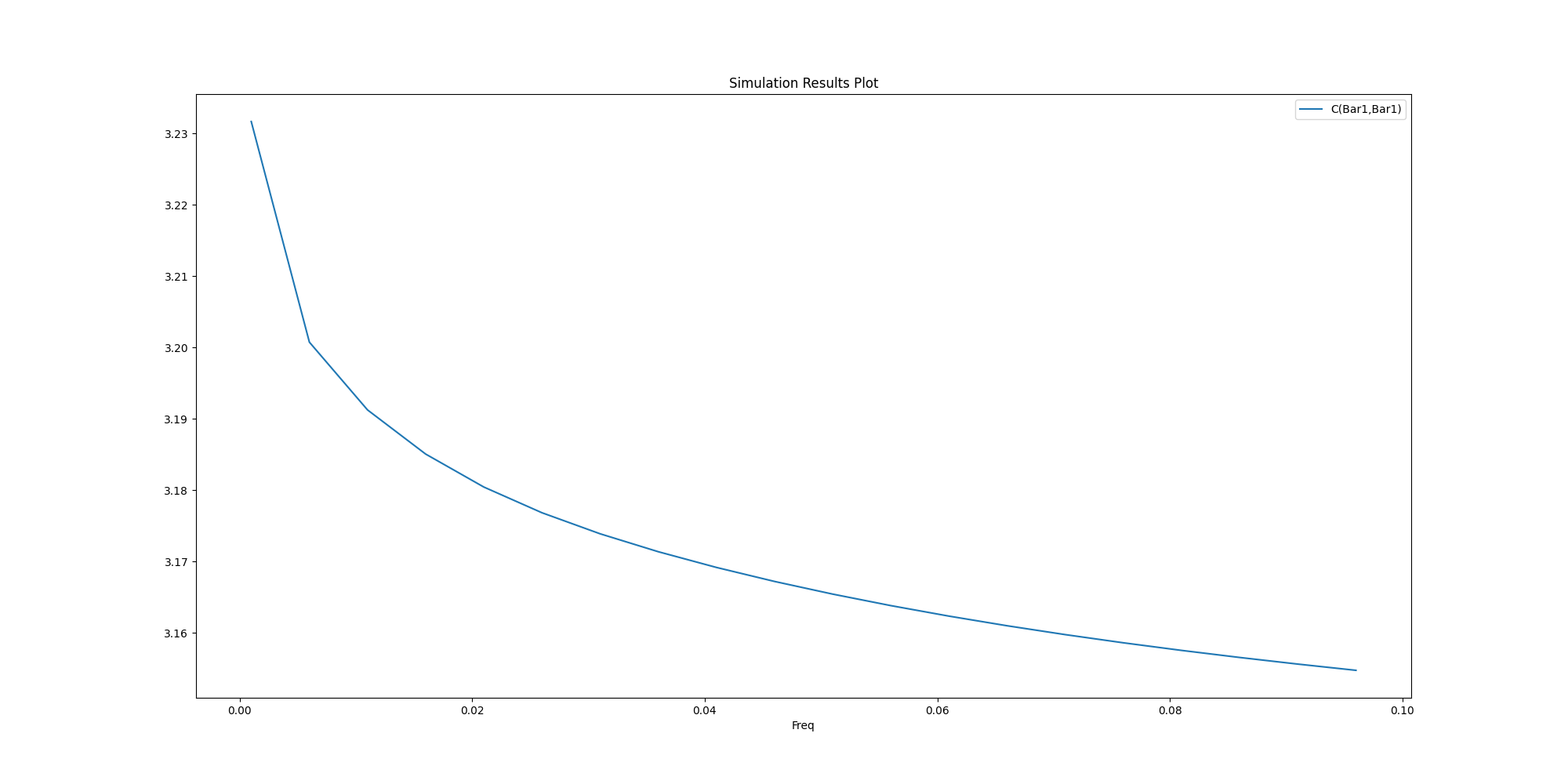
<Figure size 2000x1000 with 1 Axes>
Close AEDT#
After the simulation completes, you can close AEDT or release it using the
release_desktop method. All methods provide for saving projects before closing.
pyaedt.settings.enable_debug_logger = False
pyaedt.settings.enable_debug_methods_argument_logger = False
q.release_desktop(close_projects=True, close_desktop=True)
True
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 58.994 seconds)