Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
SBR+: HFSS to SBR+ coupling#
This example shows how you can use PyAEDT to create an HFSS SBR+ project from an HFSS antenna and run a simulation.
Perform required imports#
Perrform rquired imports and set up the local path to the path for the PyAEDT directory.
import os
import pyaedt
project_full_name = pyaedt.downloads.download_sbr(pyaedt.generate_unique_project_name(project_name="sbr_freq"))
Set non-graphical mode#
Set non-graphical mode.
You can set non_graphical either to True or False.
non_graphical = False
Define designs#
Define two designs, one source and one target, with each design connected to a different object.
target = pyaedt.Hfss(
projectname=project_full_name,
designname="Cassegrain_",
solution_type="SBR+",
specified_version="2023.2",
new_desktop_session=True,
non_graphical=non_graphical
)
source = pyaedt.Hfss(projectname=target.project_name,
designname="feeder",
specified_version="2023.2",
)
Initializing new desktop!
Returning found desktop with PID 14156!
Define linked antenna#
Define a linked antenna. This is HFSS far field applied to HFSS SBR+.
target.create_sbr_linked_antenna(source, target_cs="feederPosition", fieldtype="farfield")
<pyaedt.modules.Boundary.NativeComponentObject object at 0x000001D983FC7760>
Assign boundaries#
Assign boundaries.
target.assign_perfecte_to_sheets(["Reflector", "Subreflector"])
target.mesh.assign_curvilinear_elements(["Reflector", "Subreflector"])
<pyaedt.modules.Mesh.MeshOperation object at 0x000001D98346DA20>
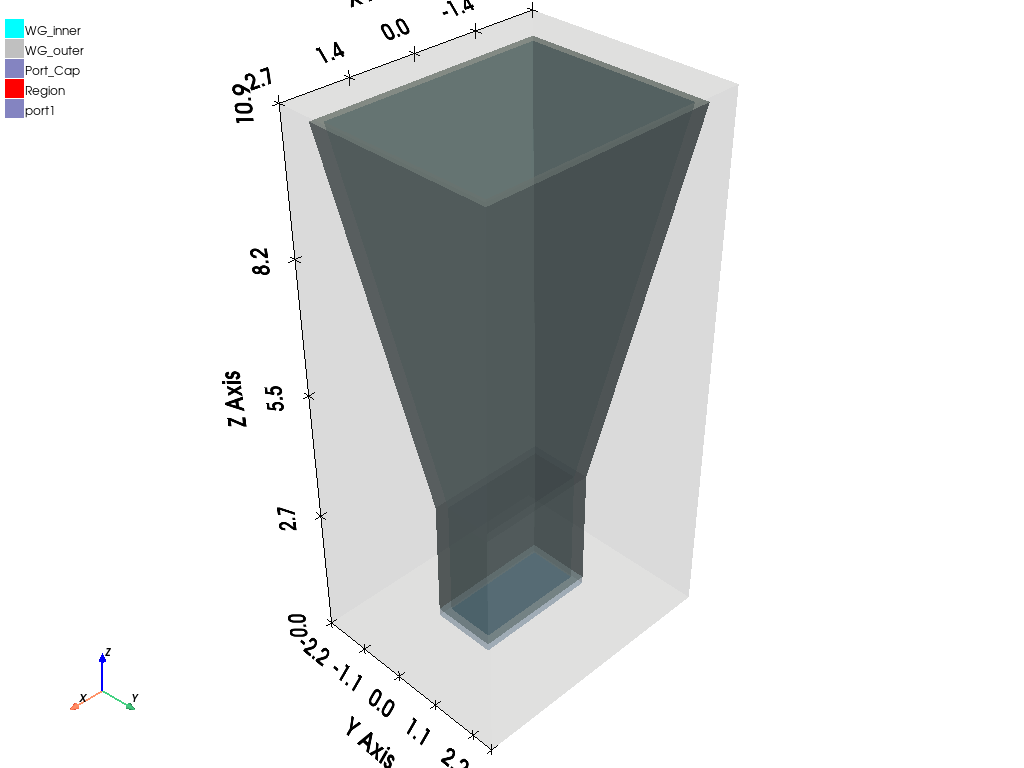
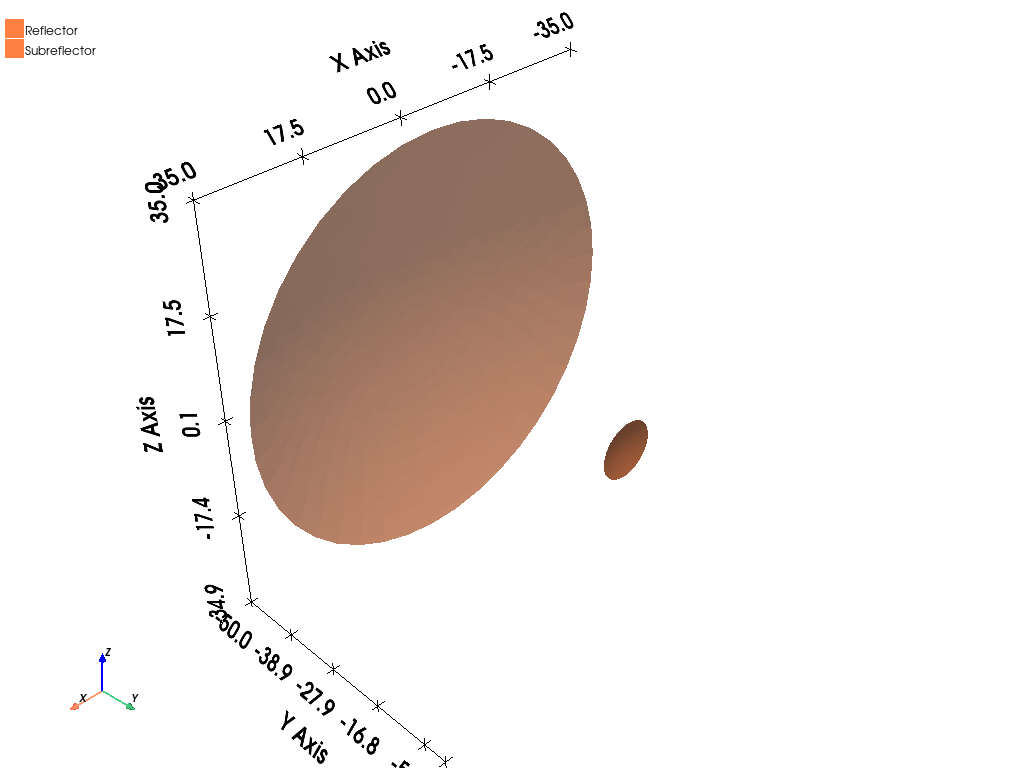
Plot model#
Plot the model
source.plot(show=False, export_path=os.path.join(target.working_directory, "Source.jpg"), plot_air_objects=True)
target.plot(show=False, export_path=os.path.join(target.working_directory, "Target.jpg"), plot_air_objects=False)
<pyaedt.generic.plot.ModelPlotter object at 0x000001D98346EEF0>
Create setup and solve#
Create a setup and solve it.
setup1 = target.create_setup()
setup1.props["RadiationSetup"] = "ATK_3D"
setup1.props["ComputeFarFields"] = True
setup1.props["RayDensityPerWavelength"] = 2
setup1.props["MaxNumberOfBounces"] = 3
setup1["RangeType"] = "SinglePoints"
setup1["RangeStart"] = "10GHz"
target.analyze()
True
Plot results#
Plot results.
variations = target.available_variations.nominal_w_values_dict
variations["Freq"] = ["10GHz"]
variations["Theta"] = ["All"]
variations["Phi"] = ["All"]
target.post.create_report(
"db(GainTotal)",
target.nominal_adaptive,
variations=variations,
primary_sweep_variable="Theta",
context="ATK_3D",
report_category="Far Fields",
)
<pyaedt.modules.report_templates.FarField object at 0x000001D98346ED10>
Plot results outside AEDT#
Plot results using Matplotlib.
solution = target.post.get_solution_data(
"GainTotal",
target.nominal_adaptive,
variations=variations,
primary_sweep_variable="Theta",
context="ATK_3D",
report_category="Far Fields",
)
solution.plot()
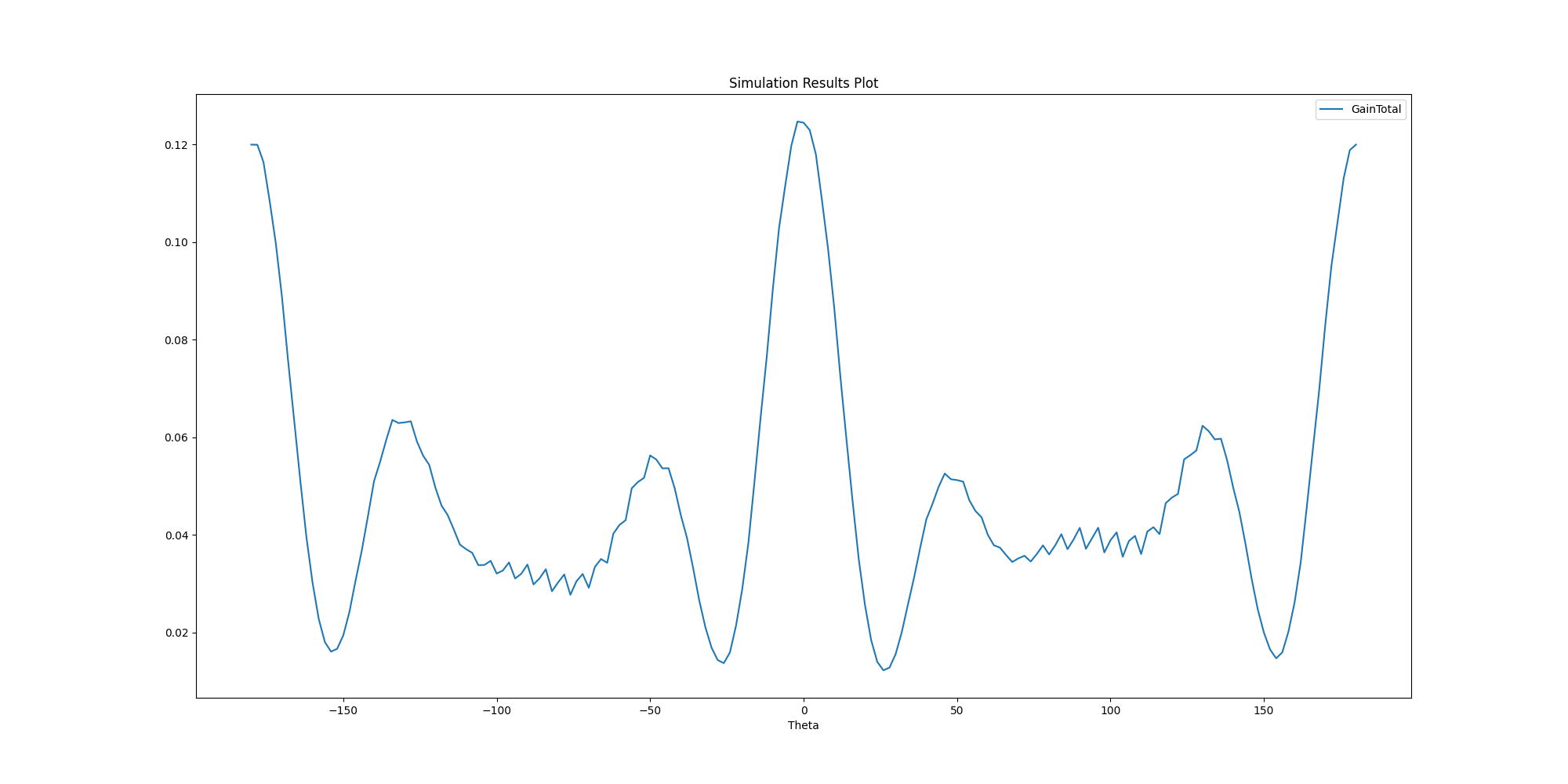
<Figure size 2000x1000 with 1 Axes>
Release AEDT#
Release AEDT and close the example.
target.release_desktop()
True
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 28.718 seconds)