Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
SBR+: doppler setup#
This example shows how you can use PyAEDT to create a multipart scenario in HFSS SBR+ and set up a doppler analysis.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports.
import os
import pyaedt
Set AEDT version#
Set AEDT version.
aedt_version = "2024.1"
# Launch AEDT
# ~~~~~~~~~~~
# Launch AEDT.
projectname = "MicroDoppler_with_ADP"
designname = "doppler"
library_path = pyaedt.downloads.download_multiparts()
Set non-graphical mode#
Set non-graphical mode.
You can set non_graphical either to True or False.
non_graphical = False
Download and open project#
Download and open the project.
project_name = pyaedt.generate_unique_project_name(project_name="doppler")
# Instantiate the application.
app = pyaedt.Hfss(
specified_version=aedt_version,
solution_type="SBR+",
new_desktop_session=True,
projectname=project_name,
close_on_exit=True,
non_graphical=non_graphical
)
app.autosave_disable()
C:\actions-runner\_work\_tool\Python\3.10.9\x64\lib\subprocess.py:1072: ResourceWarning: subprocess 7380 is still running
_warn("subprocess %s is still running" % self.pid,
True
Save project and rename design#
Save the project to the temporary folder and rename the design.
app.save_project()
app.rename_design(designname)
True
Set up library paths#
Set up library paths to 3D components.
actor_lib = os.path.join(library_path, "actor_library")
env_lib = os.path.join(library_path, "environment_library")
radar_lib = os.path.join(library_path, "radar_modules")
env_folder = os.path.join(env_lib, "road1")
person_folder = os.path.join(actor_lib, "person3")
car_folder = os.path.join(actor_lib, "vehicle1")
bike_folder = os.path.join(actor_lib, "bike1")
bird_folder = os.path.join(actor_lib, "bird1")
Define environment#
Define the background environment.
road1 = app.modeler.add_environment(input_dir=env_folder, name="Bari")
prim = app.modeler
Place actors#
Place actors in the environment. This code places persons, birds, bikes, and cars in the environment.
person1 = app.modeler.add_person(input_dir=person_folder, speed=1.0, global_offset=[25, 1.5, 0], yaw=180,
name="Massimo")
person2 = app.modeler.add_person(input_dir=person_folder, speed=1.0, global_offset=[25, 2.5, 0], yaw=180, name="Devin")
car1 = app.modeler.add_vehicle(input_dir=car_folder, speed=8.7, global_offset=[3, -2.5, 0], name="LuxuryCar")
bike1 = app.modeler.add_vehicle(input_dir=bike_folder, speed=2.1, global_offset=[24, 3.6, 0], yaw=180,
name="Alberto_in_bike")
bird1 = app.modeler.add_bird(input_dir=bird_folder, speed=1.0, global_offset=[19, 4, 3], yaw=120, pitch=-5,
flapping_rate=30, name="Pigeon")
bird2 = app.modeler.add_bird(input_dir=bird_folder, speed=1.0, global_offset=[6, 2, 3], yaw=-60, pitch=10, name="Eagle")
Place radar#
Place radar on the car. The radar is created relative to the car’s coordinate system.
radar1 = app.create_sbr_radar_from_json(radar_file=radar_lib, name="Example_1Tx_1Rx", offset=[2.57, 0, 0.54],
use_relative_cs=True, relative_cs_name=car1.cs_name)
Create setup#
Create setup and validate it. The create_sbr_pulse_doppler_setup method
creates a setup and a parametric sweep on the time variable with a
duration of two seconds. The step is computed automatically from CPI.
setup, sweep = app.create_sbr_pulse_doppler_setup(sweep_time_duration=2)
app.set_sbr_current_sources_options()
app.validate_simple()
1
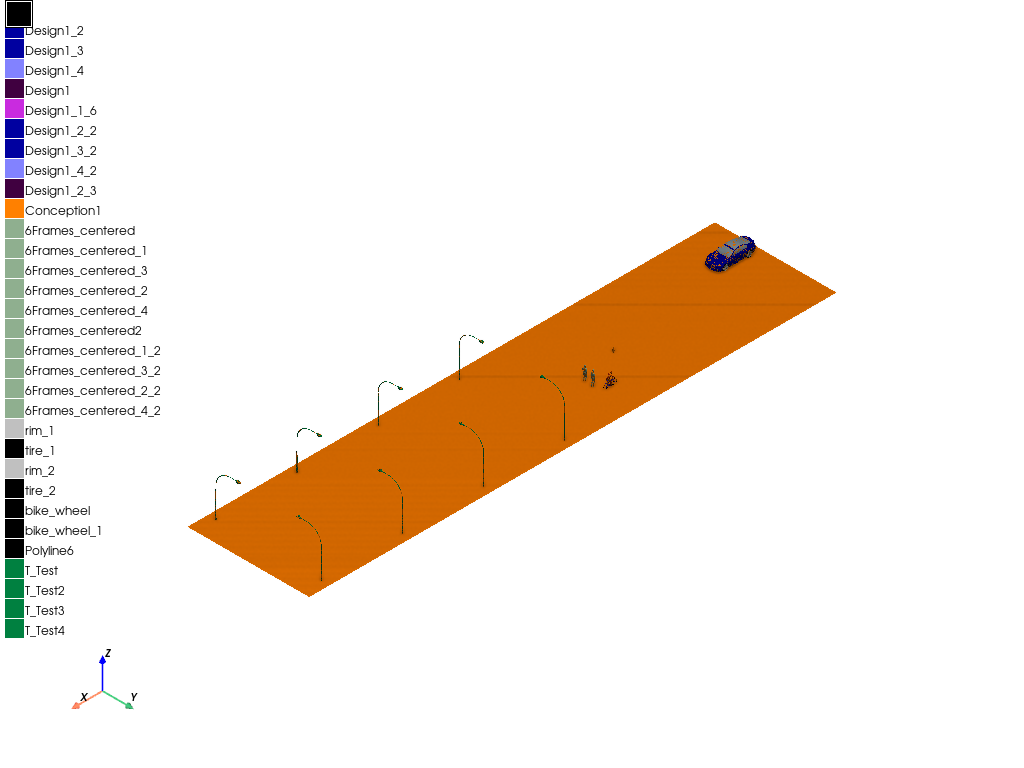
Plot model#
Plot the model.
app.plot(show=False, export_path=os.path.join(app.working_directory, "Image.jpg"), plot_air_objects=True)
<pyaedt.generic.plot.ModelPlotter object at 0x000002264A6DCA00>
Solve and release AEDT#
Solve and release AEDT. To solve, uncomment the app.analyze_setup command
to activate the simulation.
# app.analyze_setup(sweep.name)
app.save_project()
app.release_desktop(close_projects=True, close_desktop=True)
True
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 9.312 seconds)