Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
General: optimetrics setup#
This example shows how you can use PyAEDT to create a project in HFSS and create all optimetrics setups.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports.
import pyaedt
import os
Set AEDT version#
Set AEDT version.
aedt_version = "2024.1"
Set non-graphical mode#
Set non-graphical mode.
You can set non_graphical either to True or False.
non_graphical = False
Initialize object and create variables#
Initialize the Hfss object and create two needed design variables,
w1 and w2.
hfss = pyaedt.Hfss(specified_version=aedt_version, new_desktop_session=True, non_graphical=non_graphical)
hfss["w1"] = "1mm"
hfss["w2"] = "100mm"
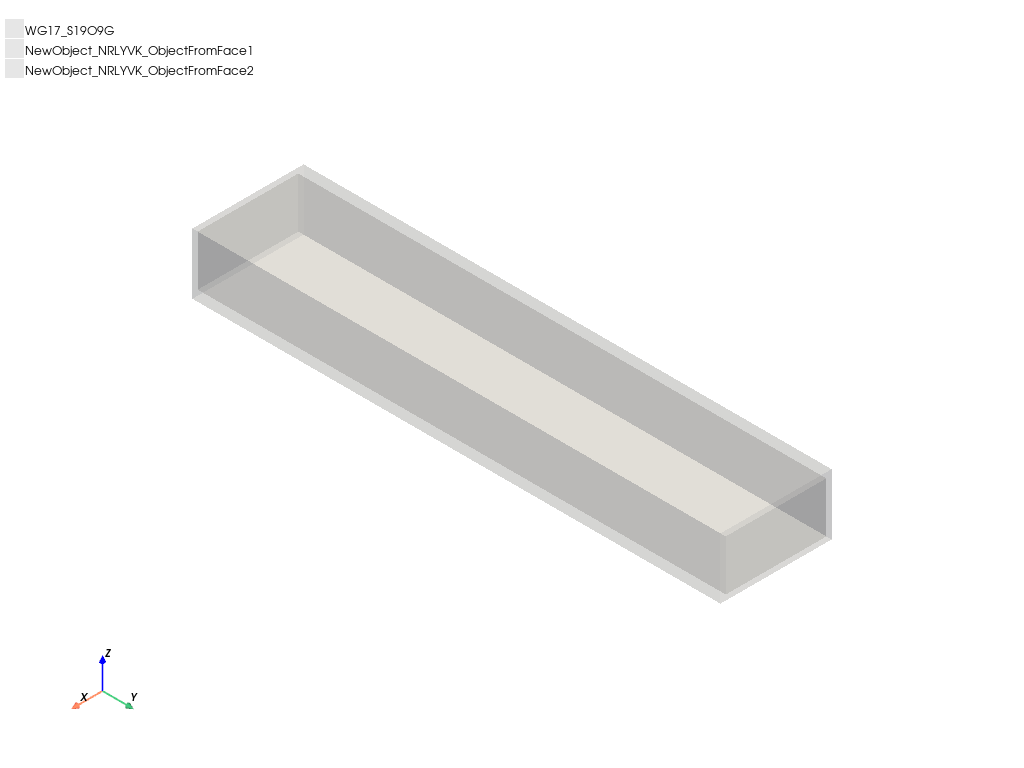
Create waveguide with sheets on it#
Create one of the standard waveguide structures and parametrize it. You can also create rectangles of waveguide openings and assign ports later.
wg1, p1, p2 = hfss.modeler.create_waveguide(
[0, 0, 0],
hfss.AXIS.Y,
"WG17",
wg_thickness="w1",
wg_length="w2",
create_sheets_on_openings=True,
)
model = hfss.plot(show=False)
model.show_grid = False
model.plot(os.path.join(hfss.working_directory, "Image.jpg"))
True
Create wave ports on sheets#
Create two wave ports on the sheets.
hfss.wave_port(p1, integration_line=hfss.AxisDir.ZPos, name="1")
hfss.wave_port(p2, integration_line=hfss.AxisDir.ZPos, name="2")
False
Create setup and frequency sweep#
Create a setup and a frequency sweep to use as the base for optimetrics setups.
setup = hfss.create_setup()
hfss.create_linear_step_sweep(
setup_name=setup.name,
unit="GHz",
start_frequency=1,
stop_frequency=5,
step_size=0.1,
sweep_name="Sweep1",
save_fields=True
)
Optimetrics analysis#
Create parametrics analysis#
Create a simple optimetrics parametrics analysis with output calculations.
sweep = hfss.parametrics.add("w2", 90, 200, 5)
sweep.add_variation("w1", 0.1, 2, 10)
sweep.add_calculation(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.5GHz"})
sweep.add_calculation(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.6GHz"})
Create sensitivity analysis#
Create an optimetrics sensitivity analysis with output calculations.
sweep2 = hfss.optimizations.add(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.5GHz"}, optim_type="Sensitivity")
sweep2.add_variation("w1", 0.1, 3, 0.5)
sweep2.add_calculation(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.6GHz"})
Create optimization based on goals and calculations#
Create an optimization analysis based on goals and calculations.
sweep3 = hfss.optimizations.add(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.5GHz"})
sweep3.add_variation("w1", 0.1, 3, 0.5)
sweep3.add_goal(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.6GHz"})
sweep3.add_goal(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": ("2.6GHz", "5GHz")})
sweep3.add_goal(
calculation="dB(S(1,1))",
ranges={"Freq": ("2.6GHz", "5GHz")},
condition="Maximize",
)
Create DX optimization based on a goal and calculation#
Create a DX (DesignXplorer) optimization based on a goal and a calculation.
sweep4 = hfss.optimizations.add(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.5GHz"}, optim_type="DesignExplorer")
sweep4.add_goal(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.6GHz"})
Create DOE based on a goal and calculation#
Create a DOE (Design of Experiments) based on a goal and a calculation.
sweep5 = hfss.optimizations.add(calculation="dB(S(1,1))", ranges={"Freq": "2.5GHz"}, optim_type="DXDOE")
Create DOE based on a goal and calculation#
Create a DOE based on a goal and a calculation.
region = hfss.modeler.create_region()
hfss.assign_radiation_boundary_to_objects(region)
hfss.insert_infinite_sphere(name="Infinite_1")
sweep6 = hfss.optimizations.add(
calculation="RealizedGainTotal",
solution=hfss.nominal_adaptive,
ranges={"Freq": "5GHz", "Theta": ["0deg", "10deg", "20deg"], "Phi": "0deg"},
context="Infinite_1",
)
Close AEDT#
After the simulaton completes, you can close AEDT or release it using the
pyaedt.Desktop.release_desktop() method.
All methods provide for saving the project before closing.
hfss.release_desktop()
True
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 55.182 seconds)